Since September 2023 is the new Swiss Data Protection Act in force. Many companies are unsure about what this means for their IT infrastructure. In this article, you will learn about the data protection issues that can arise when using a cloud and we will show you possible solutions. Solutions in order to Cloud and DSG under one roof to bring.
First of all, it should be noted that this blog post cannot and should not be used as a legal source for dealing with the Swiss Data Protection Act. However, you will find helpful information here on how to use the cloud in compliance with data protection law as well as a list of the most important sources regarding data protection law that you should consult for good protection.
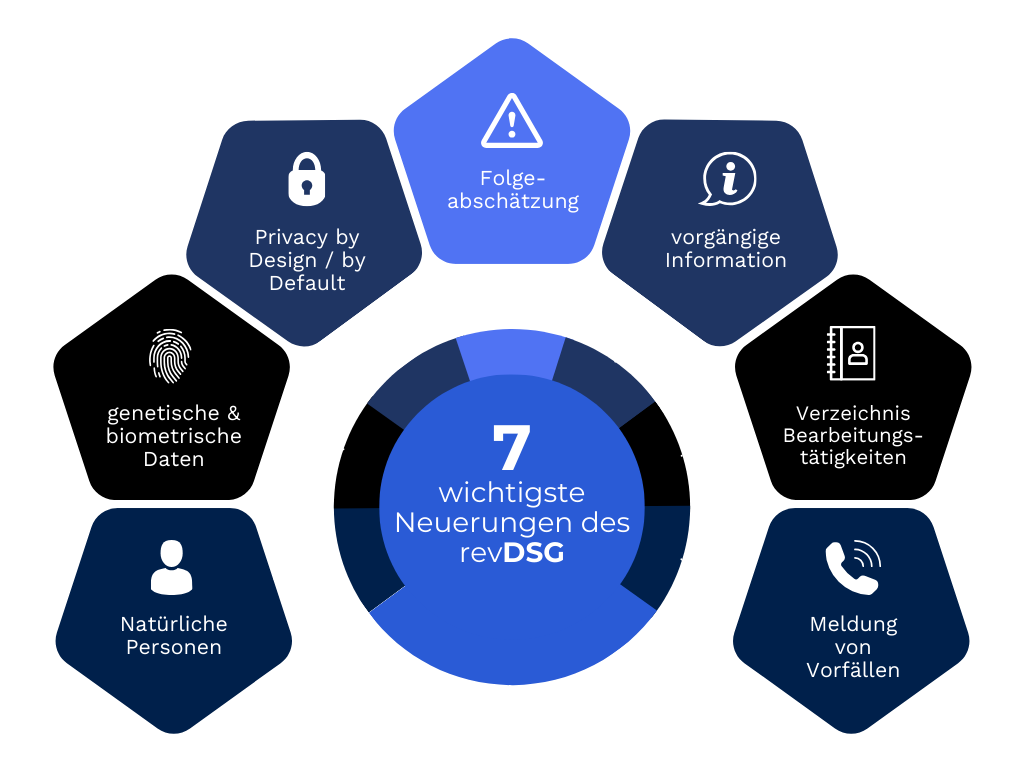
Key points of the revised Data Protection Act (revDSG)
SECO cites the following points as the most important changes for Swiss SMEs resulting from the new data protection law:
- Natural persons are the focus, data of legal persons are no longer affected.
- Genetic & biometric data are now also particularly worthy of protection.
- «Privacy by design" and "Privacy by default" must be taken into account as standard.
- If there is a high risk of personal injury or the fundamental rights of individuals being violated, a Impact assessment be created.
- The procurement of all personal data must be informed in advance become.
- A List of processing activities of personal data must be created, with the exception of certain SMEs.
- Data security breaches must be submitted to the Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner (FDPIC) as soon as possible reported become.
You can find out more in the SECO article.
Data protection issues in the public cloud
For many companies, outsourcing data and services to a public cloud solution is an important step in their digitalisation strategy. SMEs are also increasingly keen to benefit from the advantages of a cloud. However, in addition to all the advantages, the disadvantages and risks associated with such outsourcing should not be forgotten. One major risk concerns the handling of data protection, which has become even more acute with the entry into force of the new Swiss Data Protection Act.
What data protection factors need to be considered when using a public cloud?
Storage locationData in a public cloud is often stored in server centres in different geographical regions. You normally have no control over where exactly your data is physically located. According to Art. 16 FADP, the outsourcing of data abroad is only permitted if the country has been declared secure by the Federal Council or if data protection can be guaranteed by other means. In special cases, it is also prohibited to store personal data outside of Switzerland.
ResponsibilityThe responsibility for compliance with the Data Protection Act still lies with you, even if the data is outsourced to a processor.
ControlYou are obliged to regularly check the security of your data. Such checks can be very difficult, especially for large companies abroad.
FlexibilityMost public cloud solutions are standardised and cannot be flexibly adapted to your specific needs.
AccessesYour cloud must be accessible to you without interruptions. Access must also be controllable and restrictable.
SecurityData in your public cloud must be protected against unwanted changes, theft or deletion. This also includes a backup solution. As a rule, public cloud providers offer security solutions that you should definitely use.
All these points and other details must be clarified by means of contracts between you and the processor of the data. Nevertheless, you must ultimately trust that the processor will adhere to the contracts, as you often only have very limited influence over how your data is handled by a public cloud provider.
What do companies need to consider with public cloud providers?
As an entrepreneur, you are obliged, when outsourcing data storage and maintenance to a processor, to provide a Careful selection of the service provider, the order processor to instruct carefully and to check carefully. The following points should be observed:
- Encrypt your data for transfer to your cloud provider, as well as for storage.
- Anonymise or pseudonymise your data where possible in order to protect it better.
- When selecting your future public cloud provider, pay attention to Industry-specific certifications such as the ISO-27701 standard.
- Get References to potential contractual partners.
- Conclude a contract with legal support Contract for order processing which covers all important points such as data storage location, confidentiality, processing only on instruction and backup solution.
- Make sure that the order processor only works after In consultation with you, use subcontractors can.
- Clarify exactly how your data must be handled in order to comply with the Swiss Data Protection Act and any other data protection laws such as the GDPR. Provide these Instruction to the processor.
- Control You must regularly ensure that your data is stored and processed in accordance with the contract.
- Ask for Audit reports and an annual Management commitment to.
- Make sure that your order processor has Confidentiality of employees committed.
- Clarify in advance how your cloud service provider will help you with information procedures or reporting procedures.
Further tips and information:
What alternatives are there?
One Private cloud offers a good alternative to the public cloud. It differs from a public cloud solution in that the Your company's data protected from other data on a separate cloud. This makes the Security and privacy supported. There are two ways to set up a private cloud:
1. external private cloud
With the external private cloud on the infrastructure of an order processor A specially isolated cloud is set up for an individual company or organisation. This can be accessed via the internet. In contrast to the public cloud, your company's data is therefore Completely isolated from other companies and the cloud can respond better to your individual needs become. However, such a solution is often noticeably more expensive than a "normal" public cloud.
2. on-prem private cloud
An on-premise private cloud becomes on the infrastructure of your company set up. You can access the data in the private cloud via the Internet or an internal network, allowing you to even in the event of an Internet outage can still access your data. The private cloud can Completely customised to your needs what the Compliance with data protection law greatly simplified. Your data is only with you and you can thus avoid various data protection problems and still benefit from the advantages of a cloud.
However, it is important that the private cloud is either operated internally by Specialists is installed and managed by Swissmakers, or that you call in external specialists such as Swissmakers GmbH. This is the only way your on-premise private cloud can be operated securely and reliably on your own server. Learn more More about the advantages of our private cloud solution and get in touch today for a free consultation.
Free advice
Conclusion
The use of a Public cloud solution gives Some things to consider in terms of data protection. The risk can be minimised through thorough clarification, legally well-drafted contracts and good advice from specialists. With regard to data protection, the Use of a private cloud (especially on-prem) is the better solution, as here the complete control over the data is in the hands of the respective company, whereby the Compliance with data protection law simplified becomes.